Where are we going with this? The information on this page should increase understanding related to this standard: Identify patterns of inheritance to predict genotype/phenotype and solve punnett square problems.
Article includes ideas, images, and content from Troy Smigielski (2022-01)
Human DNA Analysis
(Sort of digging in deep, eh?)
Using DNA technology and a genome database, scientists can detect specific sequences in DNA that are linked to known genetics or genetic disorders.
They could also be the first to link a sequence to a trait.
Lots of words… wow!
A genome is a complete set of genes in an organism.
Since we are talking about DNA, it is probably worth a few words to review how DNA forms.
…a purine will ALWAYS bond with a pyrimidine.…the A pairs with T or U.…the C pairs with G.…the number of A and T is always the same.…the number of C and G is always the same.
The nitrogen base will be A, G, C, or T (in DNA).
If the base is A, then there will be a T on the other side of it.
Likewise for C and G
DNA analysis looks at the sequences of the pairs, and from that, can learn things about the genetic structure of an organism.
Why would prospective parents decide to have genetic testing?
Prospective parents are often sequenced to test for the presence of genetic disorders.
You might be surprised to know that the DNA between any two humans is exactly the same.
DNA fingerprinting is a technique that identifies unique patterns in a person's DNA. On average, about 99.9% of DNA is the same between two humans. The remaining 0.1% is what is targeted in DNA fingerprinting.
Sounds like there's not much to go on! This 0.1% is still 3 million base pairs.
How could this be useful in real life?
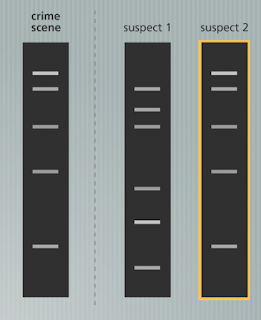
DNA fingerprinting can be especially helpful in solving crimes.
Forensic scientists can sequence DNA left behind at a crime scene and try to match it to a suspect.
What if you find a suspect with an identical twin?
That's not always a problem! Mutations often arise that can distinguish between the two twins.
Several things can be used to collect a DNA sample. A few are:
- Blood
- Sperm
- Hair with tissue
- Saliva
- Any body tissue that is not degraded
What do lab scientists do with one of these samples?
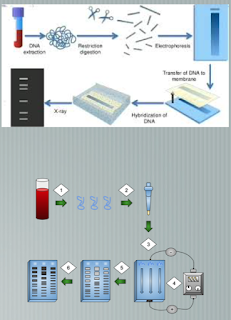
PCR uses technology to produce many copies of a small amount of DNA. It amplifies DNA.
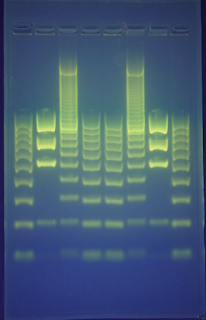
Once PCR is done and several copies are made, DNA is separated based on length using gel electrophoresis.
Gel Electrophoresis Examples
The Human Genome Project is a research program aimed at mapping all of the genes in the human body. One goal of this is to identify functions of all genes and proteins so that we can understand them.
If this project is successful, it could greatly impact the medical field and biotechnology companies. There are many implications for the findings of this research.
Gene Therapy
Gene therapy is a process that identifies the problematic gene(s), targets them and changes it. Viruses are often used to carry the normal genes into cells.
This is because they hijack your cells and insert their DNA.
The goal is to repair the DNA in a non-functioning cell so that future mitosis does not repeat the irregularity.
Genetically Modified Organisms: GMOs
Genetically modified organisms can provide alternatives that have the potential to increase productivity, making good cheaper and more readily available. GMOs, however, are the focus of much controversy and concern.








No comments:
Post a Comment